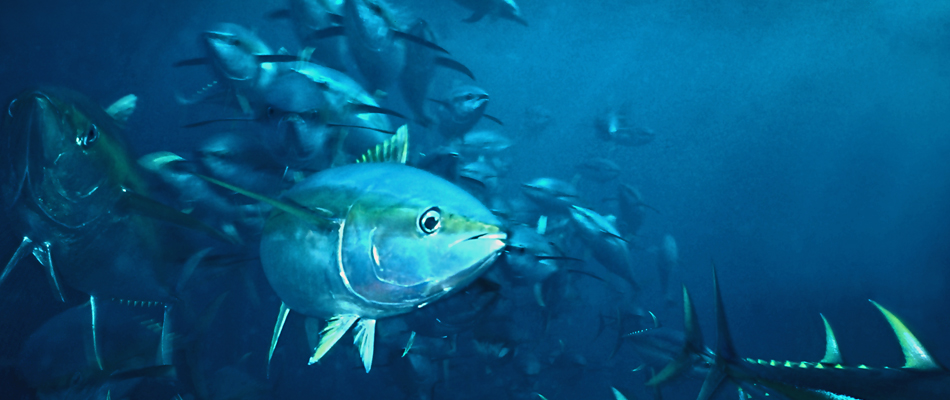
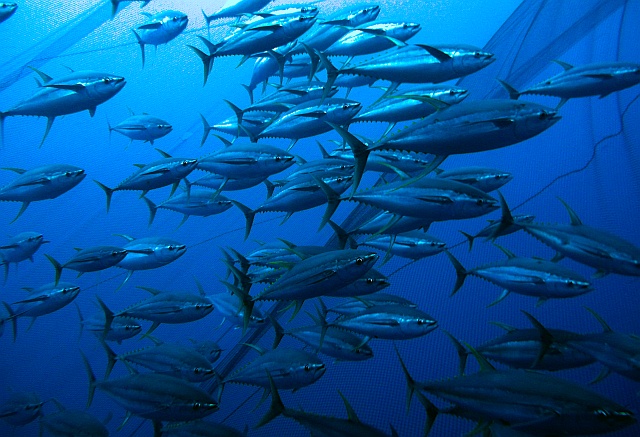
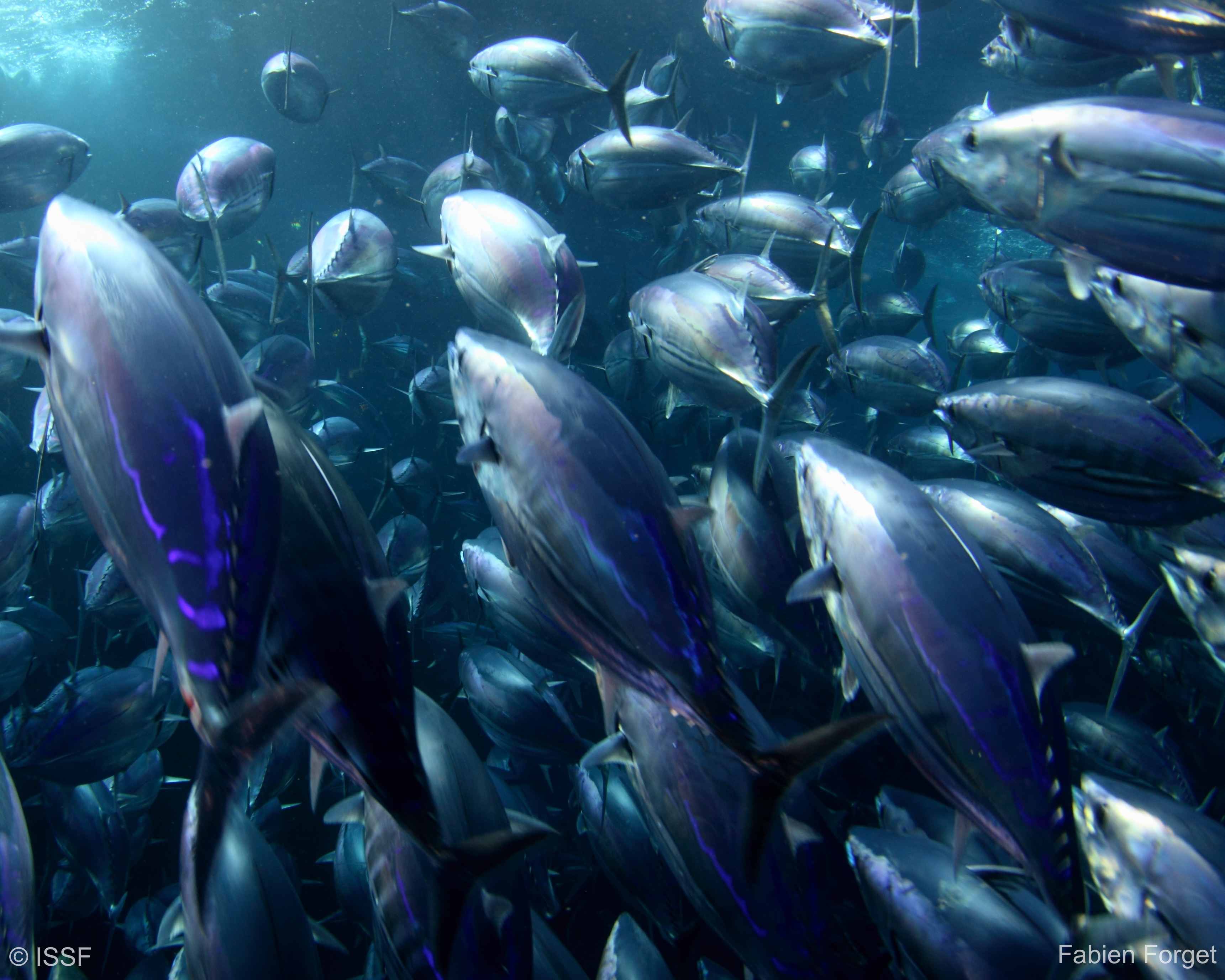
Yellowfin
Yellowfin (Thunnus albacares) are found in the tropical and subtropical areas of the Atlantic, Indian, and Pacific Oceans. Yellowfin reach intermediate sizes, between albacore and bigeye.
In: FAO Species Catalogue, Vol. 2. Scombrids of the World (1983). Courtesy of Fisheries and Aquaculture Department/Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations.
They form both free and associated schools, with adults generally forming schools of similarly sized individuals. The free-swimming schools tend to contain large individuals and are mono-specific. In the Eastern Pacific, schools are often associated with dolphin pods, which is not common elsewhere.
Yellowfin accounted for about 31% of the 5.2-million-tonne global tuna catch in 2023.
Species Characteristics
| Size (cm) | Weight (kg) | Age (yrs) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Common | 40–170 | 1.2–100 | |
| Maximum | 205 | 194 | 18 |
| Maturity | 85–108 | 12–26 | 2–3 |
| Generation Length |
4–5 |
Geographic Limits
- From 45°–50° N and S, although in the Pacific Ocean they occur mainly from 20° North and South
Species Management
The following four yellowfin stocks are assessed and managed by the RFMOs:
- Atlantic Ocean
- Eastern Pacific
- Western Pacific
- Indian Ocean
Yellowfin Tuna Stock Status
Our Status of the Stocks report summarizes the status of yellowfin tuna worldwide according to the most recent scientific assessments.
It also reviews the management measures for yellowfin that Regional Fisheries Management Organizations (RFMOs) have adopted.
RELATED RESOURCES

Interactive Stock Status and Catch Tool
Use our interactive data-visualization tool to create and then download or share graphics on tuna stock status.
You can visualize data on 23 commercial tuna stocks (by species and ocean area) share of total catch, stock health trends, and catch trends over time.

ISSF 2025-08: An Evaluation of the Sustainability of Global Tuna Stocks Relative to Marine Stewardship Council Criteria
The Marine Stewardship Council scoring system was used to evaluate 23 stocks of tropical and temperate tunas, including the bluefin tuna stocks (added in 2021), throughout the world.
Yellowfin Stock Health & Catch Trends
Use our “Interactive Stock Status and Catch Tool” to visualize, download, and share data about yellowfin tuna:
- Stock health since 2011
- Current catch by fishing method
- Catch trends by fishing method since 1950
Tuna Conservation
Our research and advocacy work aims to ensure, on a global level, that tuna resources are well managed and protected from overfishing.
Tuna Stock Evaluations
An ISSF report uses the Marine Stewardship Council (MSC) scoring system to evaluate both the health and RFMO management of 23 tuna stocks worldwide, including bluefin.


