Commission for the Conservation of Southern Bluefin Tuna (CCSBT)
The Commission for the Conservation of Southern Bluefin Tuna (CCSBT) is governed by the Convention for the Conservation of Southern Bluefin Tuna and is responsible for the management of southern bluefin tuna throughout its range.
Beginning in the 1980s, several nations (Australia, Japan and New Zealand) began to apply strict quotas to their fishing fleets to address the need to conserve and manage Southern bluefin tuna stocks in the Southern Pacific.
In 1994, this voluntary group was formalized, creating CCBST. Since CCBST’s inception, the Republic of Korea, Indonesia, the Fishing Entity of Taiwan, Philippines, South Africa and the EU joined the RFMO as members or cooperating non-members.
Stock Status & Management Measures

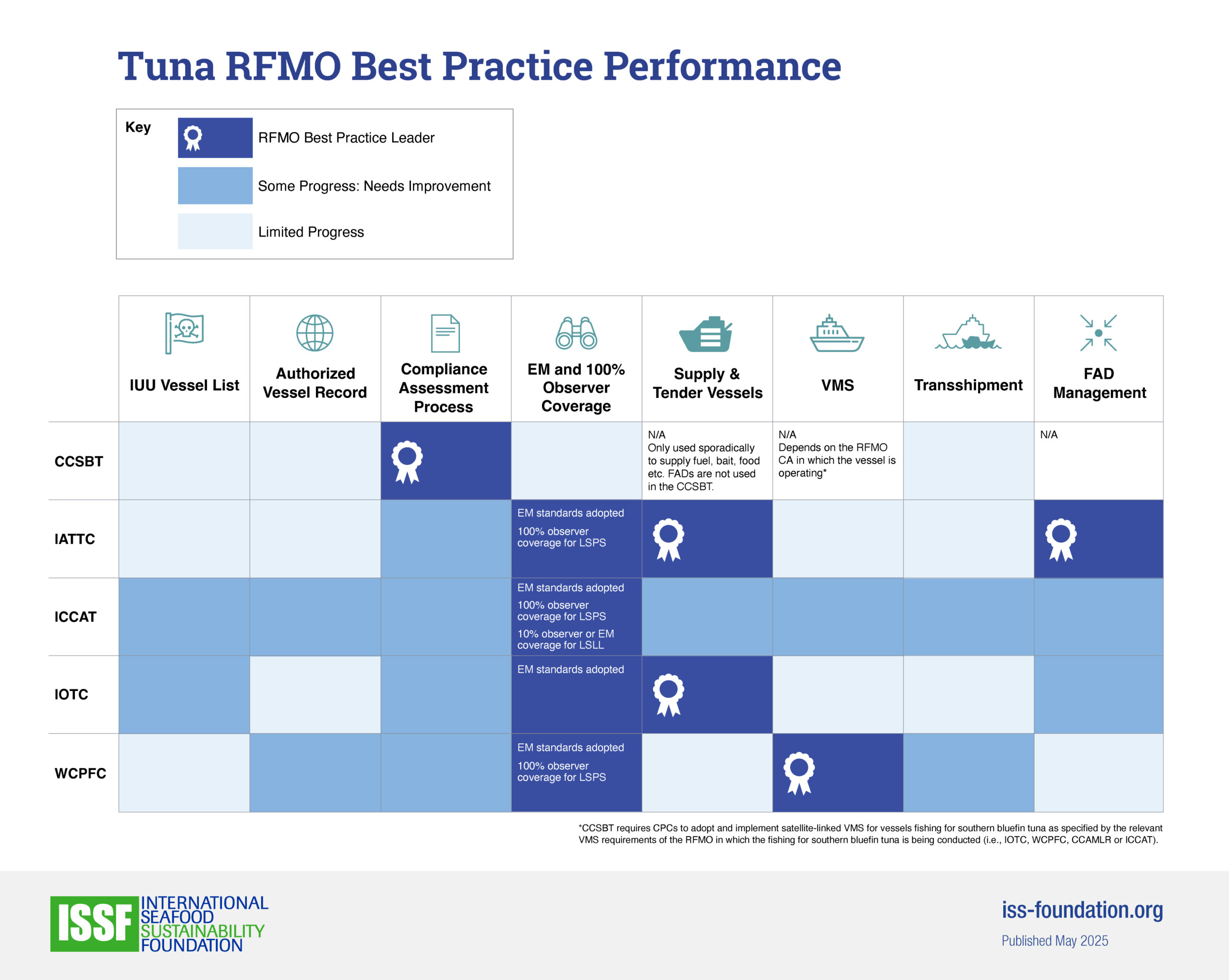
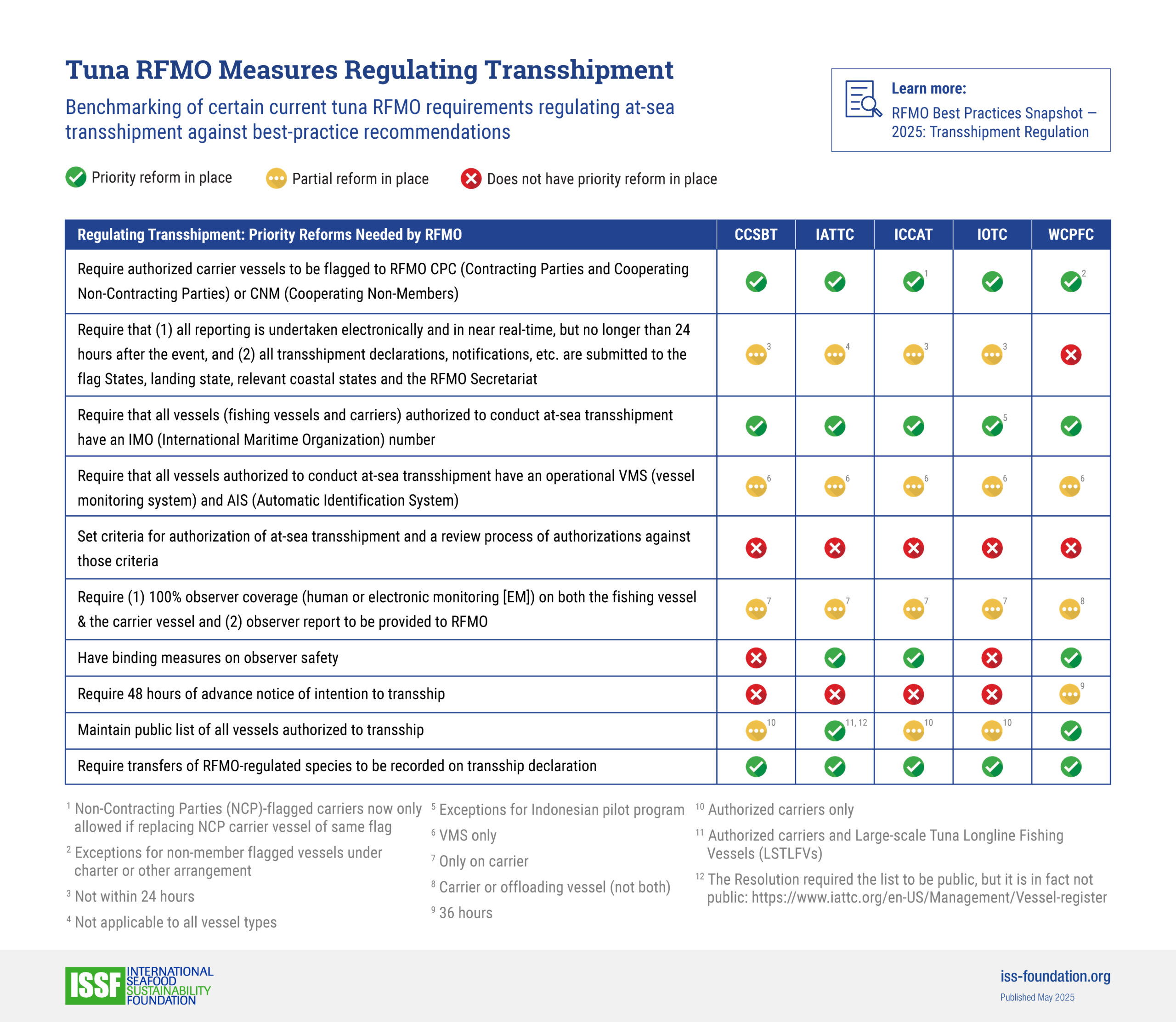
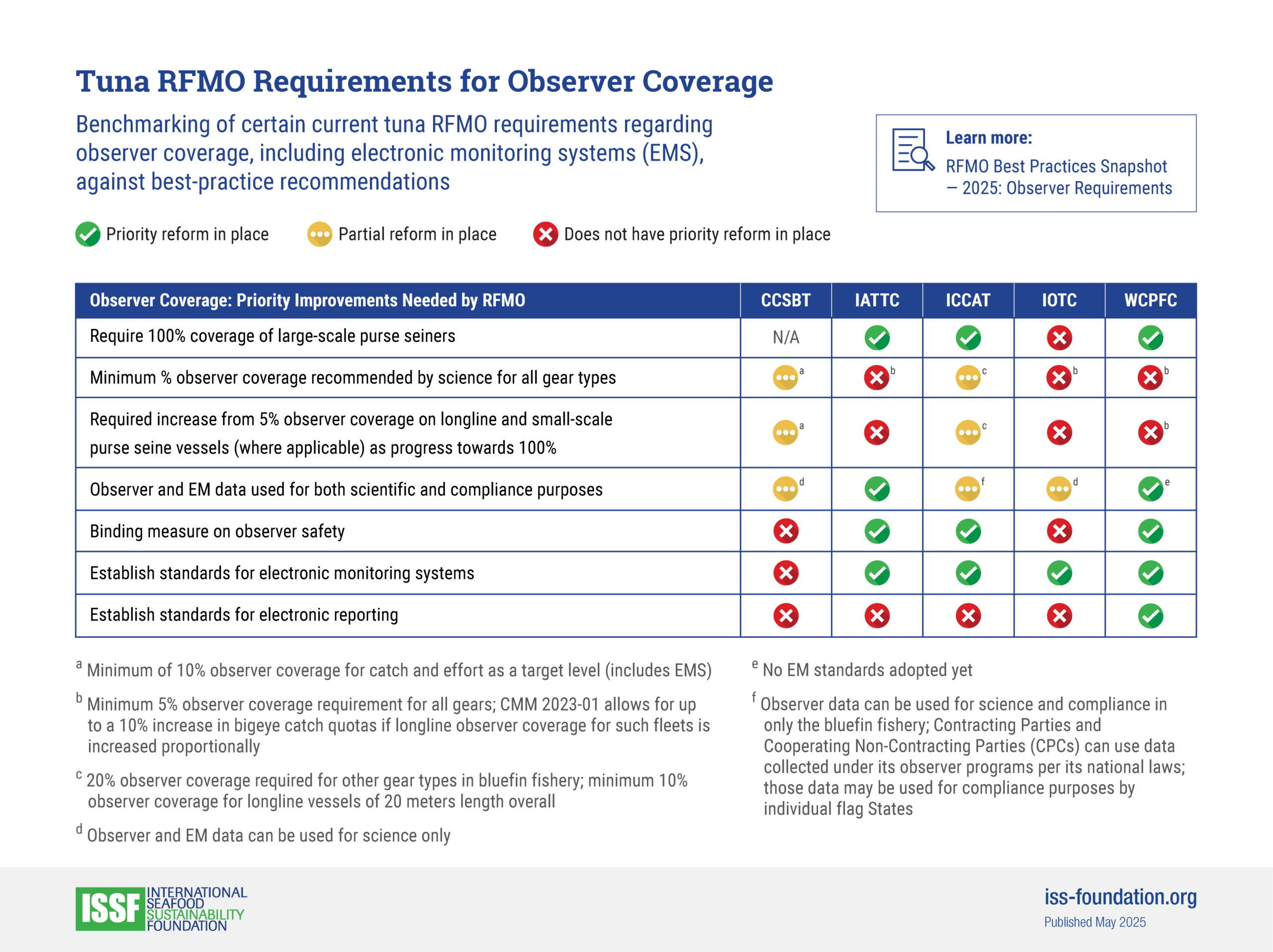
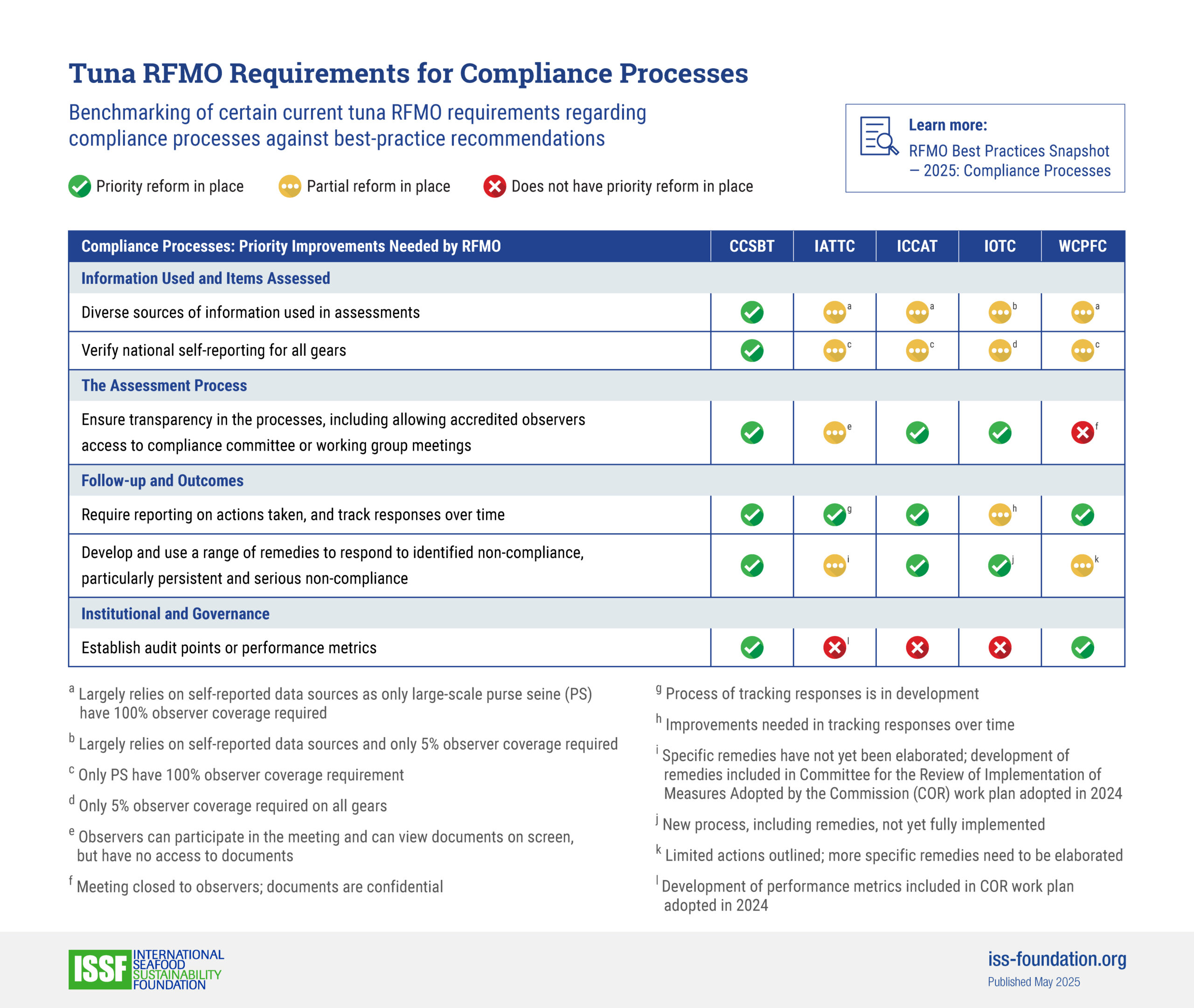
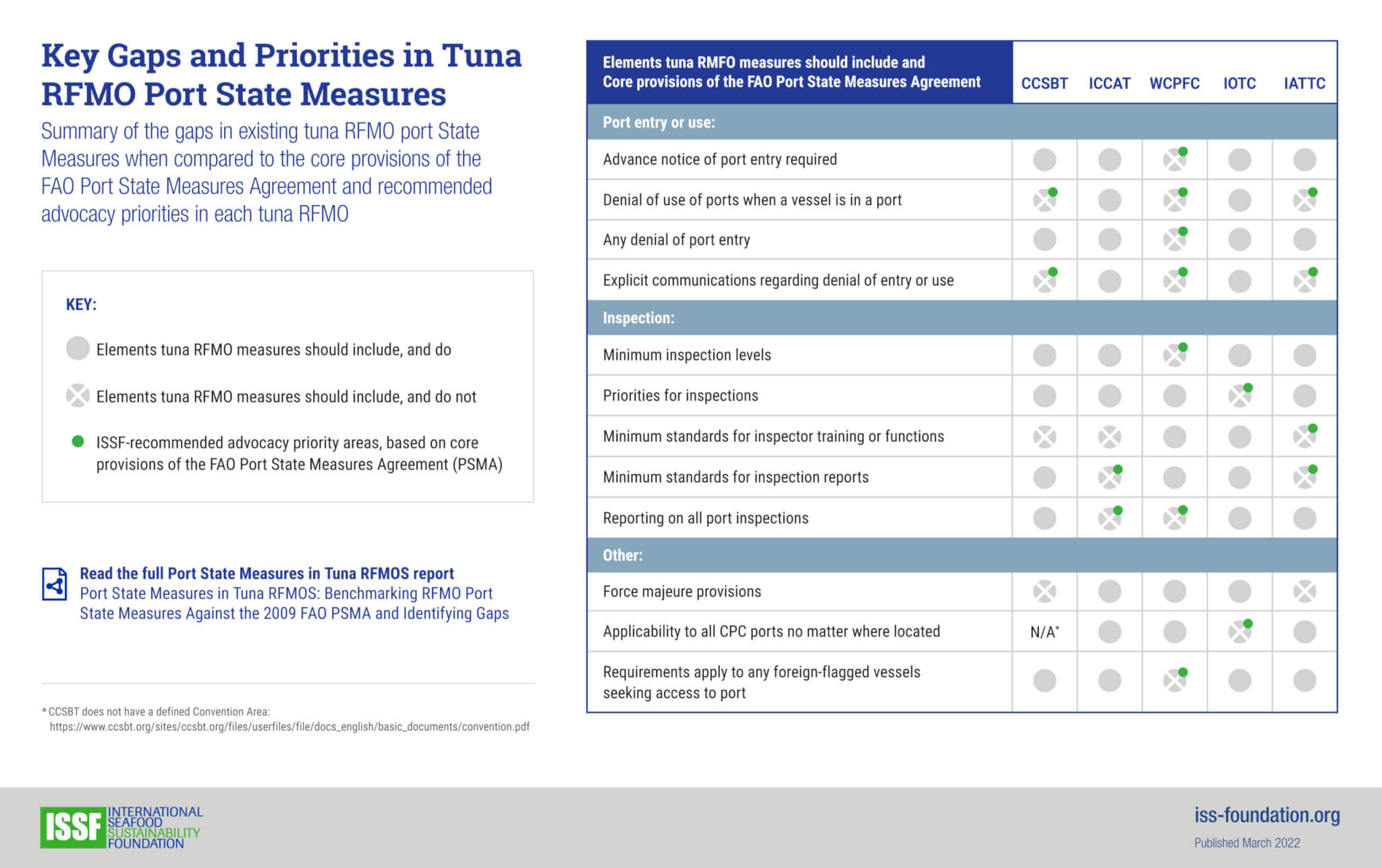
- ISSF benchmarks the tuna-fishery policies of CCSBT and other tuna RFMOs to a series of best practices we document in reports and “snapshots.”
- We also issue detailed position statements for each RFMO to help guide decision-making at their annual meetings, which ISSF scientists and policy experts often attend.
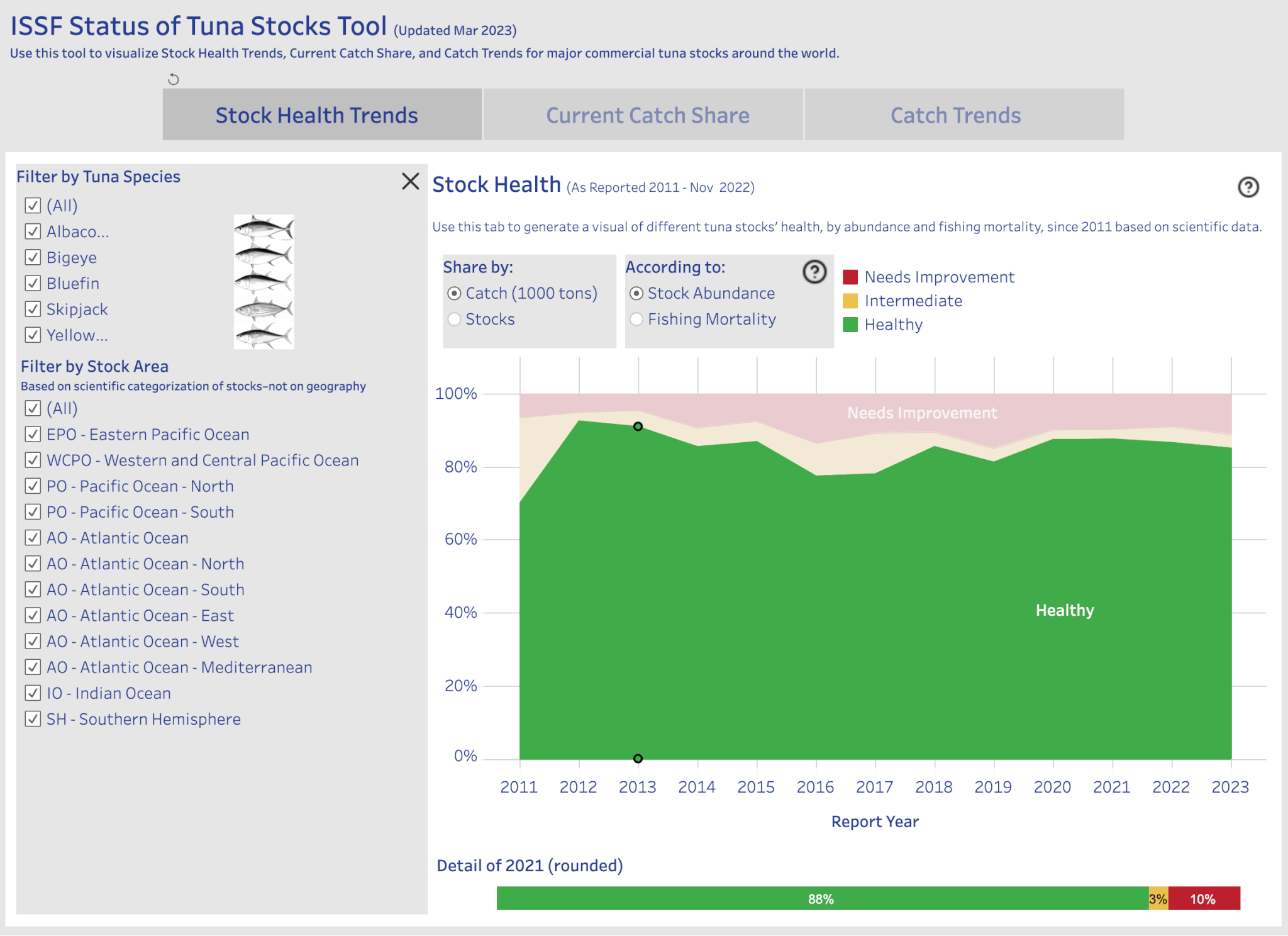
- In addition, we produce a “Status of the Stocks” report, which summarizes and rates the status and management of 23 major commercial tuna stocks, and an “Interactive Stock Status and Catch” tool.
- Our report ISSF 2025-02: Tuna Fisheries’ Impacts on Non-Tuna Species and Other Environmental Aspects: 2025 Update* examines the effects of different tuna-fishing methods, summarizing each RFMO’s related management measures for protecting both non-tuna and Endangered, Threatened, and Protected (ETP) species.
CCSBT OVERVIEW
See a list of nations that are members of CCSBT.
Article 3: "...to ensure, through appropriate management, the conservation and optimum utilisation of southern bluefin tuna."
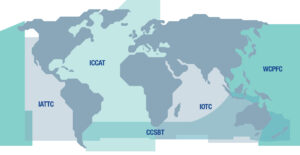
NOTE: IOTC, ICCAT and WCPFC also have responsibility for southern bluefin in their respective Convention Areas. However, since CCSBT is responsible for the species throughout its range, members of these other organizations defer to CCSBT for assessment and management of the species.
- Sharks
- Seabirds
- Sea turtles
Note: Members are expected to comply with binding and recommendatory measures on these species and other ecologically related species adopted by IOTC or WCPFC when fishing for southern bluefin tuna in those Convention Areas. Members are required to use Tori poles in all longline SBT fisheries below 30° south.
Open to States whose vessels fish for southern bluefin and to States having EEZs through which the species migrates.
The CCSBT is responsible for setting fishing quotas for the Southern bluefin tuna stock, both in terms of total allowable catch and its allocation among the member states. In this role, the CCSBT is responsible for:
- Being the coordination mechanism for member activities in the southern bluefin tuna fishery
- Considering and administering regulatory measures
- Conducting and coordinating a scientific research program to provide information in support of Commission objectives
- Supporting and implementing fishery management
- Fostering conservation activities for ecologically related species
- Providing a forum for dialogue and discussion
- Liaising with other RFMOs in areas of mutual interest
The CCSBT Convention makes no explicit mention about the Precautionary Approach or ecosystem considerations. However, the Commission requires data for non-target species. The CCSBT also has a working group on Ecologically Related Species that has begun to meet every two years and provides recommendations to the Commission.
The Scientific Committee (SC), composed of representatives from each Commission member and an independent scientific advisory panel, is responsible for all scientific work and providing scientific advice on management measures. The Secretariat plays primarily a facilitating role in organizing meetings, maintaining databases and making publications. The stock assessments are carried out by the SC. From October 2010, the Scientific Committee is required to incorporate advice consistent with the precautionary approach in its advice to the Commission.
Conservation and management measures are agreed to by consensus or unanimous vote of members present (two-thirds of members in a meeting constitutes a quorum). Binding decisions are called "Resolutions."
RELATED RESOURCES
-
CCSBT Quick Links
CCSBT at a Glance
Established: 1994
Headquarters: Canberra, Australia
Area of Competence: The area of competence is the entire geographical range of southern bluefin tuna (southern waters of the Atlantic, Indian and Pacific Oceans)
RFMO Best Practices Snapshots
See how CCSBT is performing against benchmarks for FAD management, stock management, harvest control rules, and other issues for sustainable tuna fisheries.
Tuna Catches in CCSBT's Region
Use our "Interactive Stock Status and Catch Tool" to visualize the current tuna catch — and catch trends over time — in the CCSBT region.
Download the data in different file formats, and generate custom graphics to share via email, X, or Facebook.