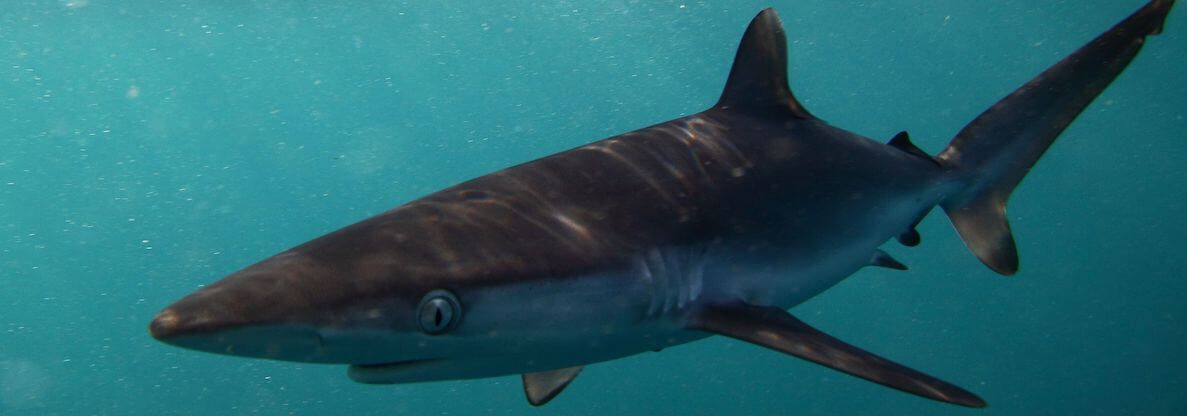
Sharks
There are three major areas of concern when it comes to sharks: observed bycatch, unobserved mortality due to entanglement in fishing gear, and difficulties in monitoring the practice of shark finning — and enforcing anti-finning measures.
Sharks are caught in purse-seine, longline, gillnet, and other tuna fisheries, usually as bycatch.
Because of their low reproductive rates and other life-history characteristics, many species of sharks are vulnerable to fishing.
Shark Bycatch
Our report summarizes risks to sharks in tuna fisheries and also reviews tuna RFMO management measures for shark conservation.

Common Shark Species in Tuna Fisheries
- Silky shark (Carcharhinus falciformis)
- Oceanic whitetip shark (Carcharhinus longimanus)
- Shortfin mako shark (Isurus oxyrinchus)
- Blue shark (Prionace glauca)
- Common thresher shark (Alopias vulpinus)
- Pelagic thresher shark (Alopias pelagicus)
- Bigeye thresher shark (Alopias superciliosus)
OUR RESEARCH & ADVOCACY
Anti-Shark-Finning Measures
Some vessels intentionally catch sharks to harvest their fins, which are valuable in certain markets. Shark finning threatens shark populations and violates the U.N. FAO Code of Conduct for Responsible Fisheries and IPOA-Sharks.
Our conservation measures 3.1(a), 3.1(b), and 3.1(c) ask ISSF participating companies to take certain steps to help prevent shark finning in the seafood industry.
Bycatch Prevention Strategies
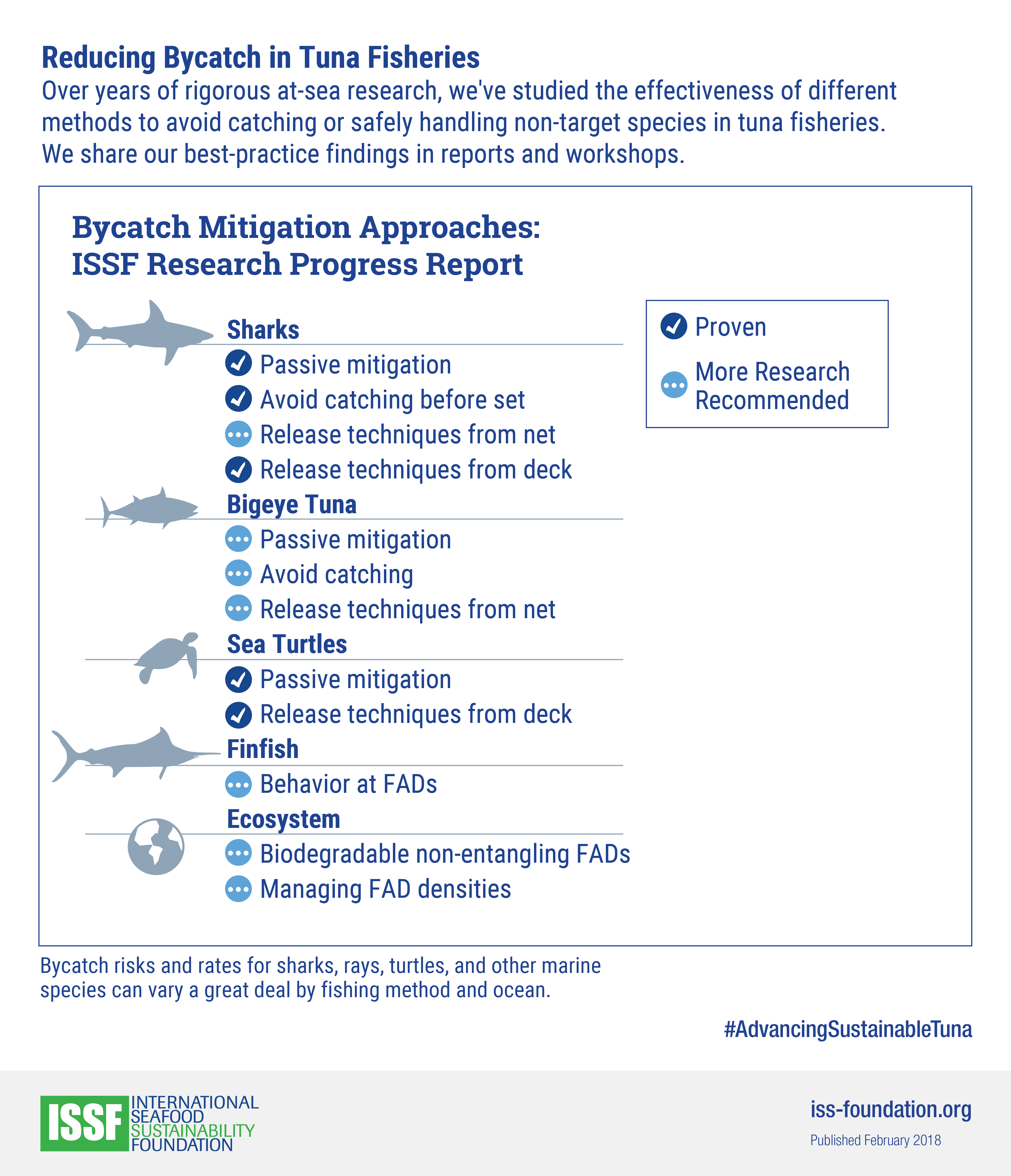
We have researched tuna fishing’s impacts on sharks and reviewed the management measures adopted by RFMOs to mitigate these impacts. Our bycatch management strategy report defines “inputs” or considerations for mitigating shark bycatch.
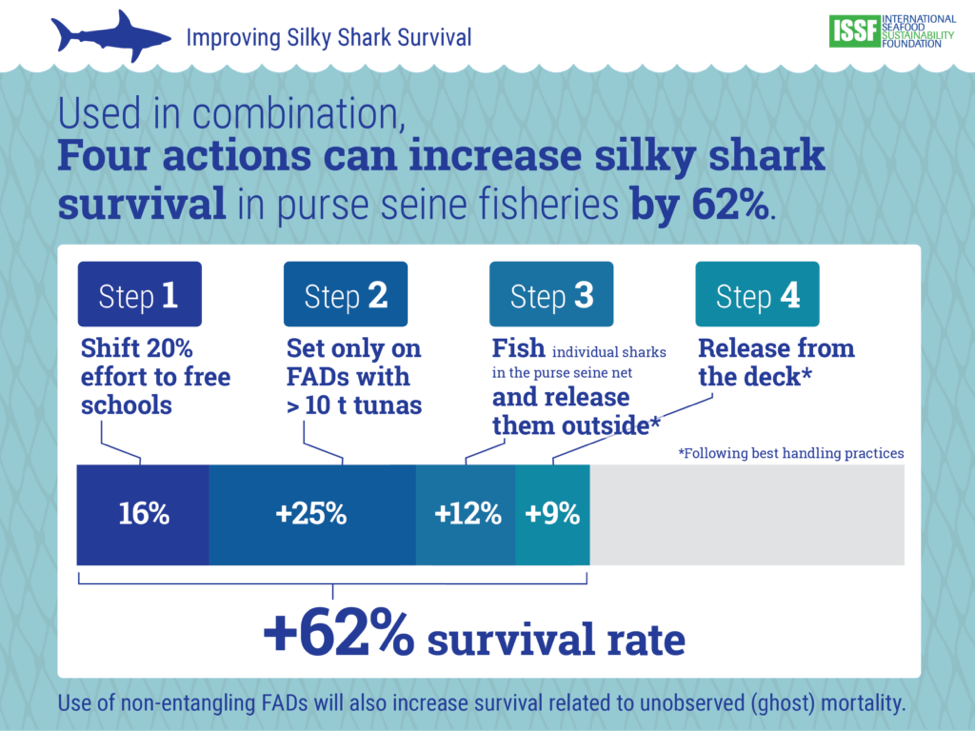
Our scientists have identified steps fishers can take before and after the tuna catch to reduce unintentional catches of silky sharks by up to 62%. We outline shark bycatch-mitigation techniques in scientific reports and skippers guidebooks.
For shark bycatch rates by ocean, see our “Tropical Purse Seine Fisheries Bycatch” infographic series.
Bycatch Handling & Release Techniques
In ISSF guidebooks, infographics, posters, and scientific reports, we publish best practices that purse-seine fishers can follow onboard to safely release live sharks from the deck. We also have compiled shark identification resources by ocean.
We also report on collaborative workshops with fishers to discuss new equipment and handling techniques for releasing accidentally caught sharks and other species.
FAD Design & Management
ISSF scientists worked with tuna fishers and physical oceanographers to develop a new model for FADs: the jelly-FAD. The jelly-FAD is safer for sharks and other marine animals because it does not use netting. It also is made with nearly 100% biodegradable materials.
To inform Regional Fisheries Management Organization (RFMO) requirements for fleets, ISSF shares science-based shark-conservation best-practices information through position statements and other outreach efforts. We also evaluate RFMO FAD management measures intended to help protect sharks.
RELATED RESOURCES
Jelly-FAD Construction Guide
Our new guide gives tuna fishers step-by-step instructions for building jelly-FADs — a new, netting-free biodegradable FAD design that reduces shark entanglement risk.
Shark Photo Gallery
View and download photos of sharks from our photo gallery, taken by ISSF scientists and scientist-consultants.
Our Shark Videos
ISSF’s YouTube channel features exclusive videos about our shark research.